The Position Property in CSS
The CSS position property is used to position an element on the web page. It has a different positioning method that is used by elements during positioning on the web page.
These positioning methods are
static,relative,fixed,absoluteorsticky.CSS Positioning Properties are:
CSS Static Positioning
CSS Relative Positioning
CSS Fixed Positioning
CSS Absolute Positioning
CSS Sticky Positioning
Elements are then positioned using the top, right, left and bottom properties. However, these properties will not work unless the position property is set first. They also work differently depending on the position value.

How to use CSS Position Properties
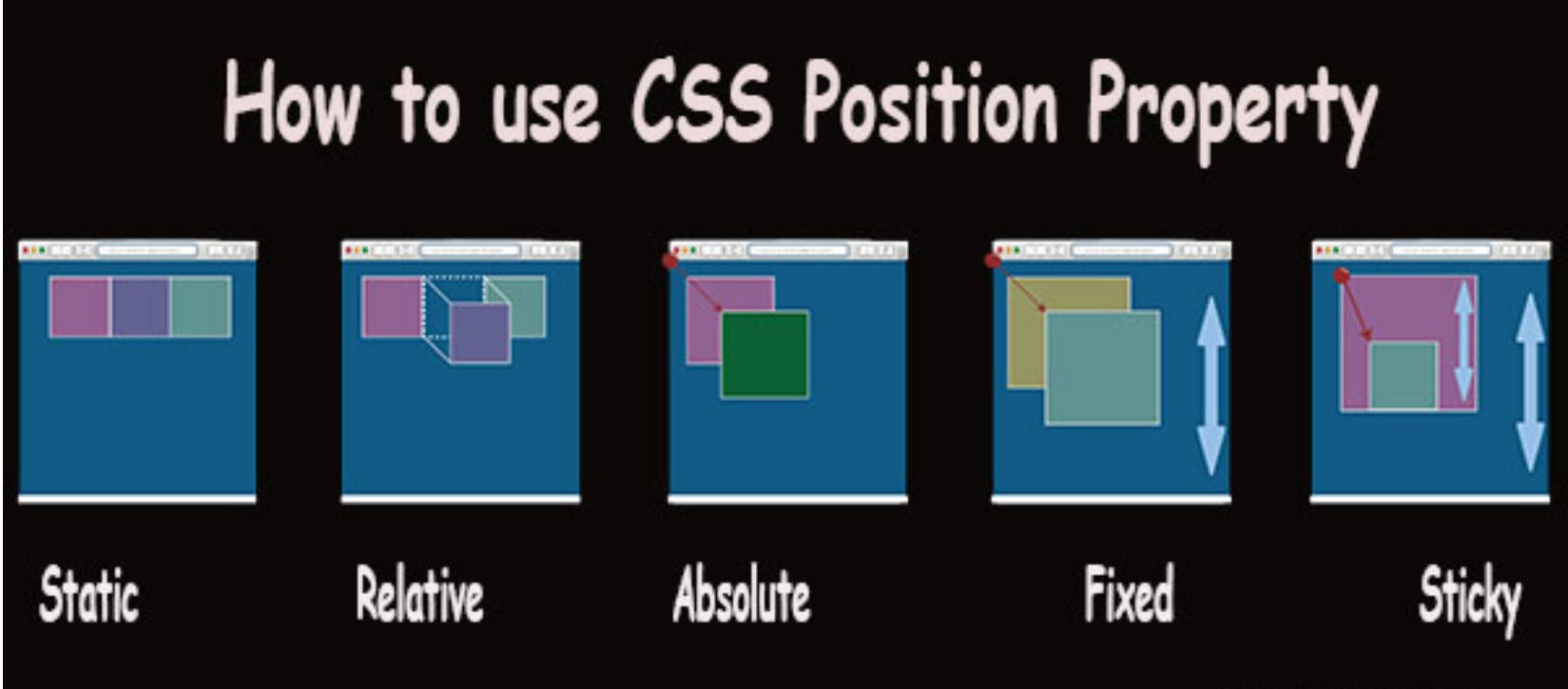
1.CSS Static Position Property
This is the default positioning of the HTML element and it is not affected by the top, bottom, left, right, and z-index properties.
An element with
position: static;is not positioned in any special way; it is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page.
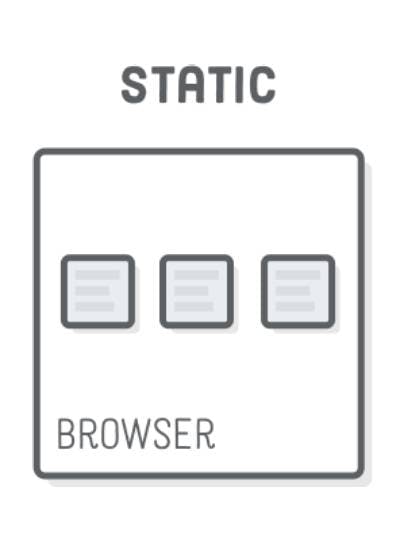
The Image shows the Static CSS Positioning property
Example:
-
In this example, CSS
position:staticproperty is used. Please keep in mind that this property is applied by default on the element. Theleft,right,top,bottomproperty can not work with the static property of position.
2.CSS Relative Position Property
The Relative positioned element is positioned itself relative to its normal position. After applying the following relative properties like
top,bottom,rightandleftthe box element will be shifted with respect to its normal position.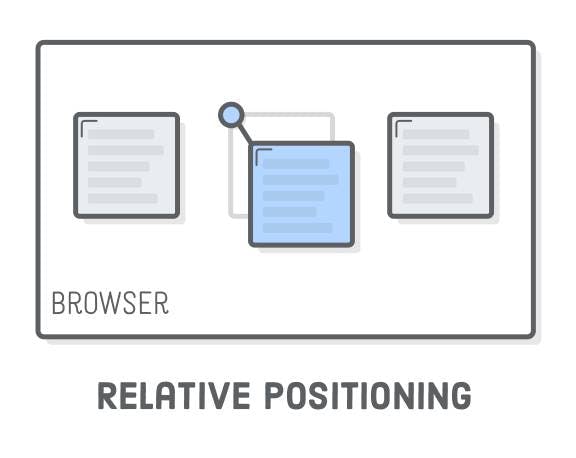
The Image shows the Relative CSS Positioning property
EXAMPLE:
-
In this example, CSS
relativeproperty of the position is used.After applying CSS relative property, the element can be shifted from its normal position after providing top and right property values.
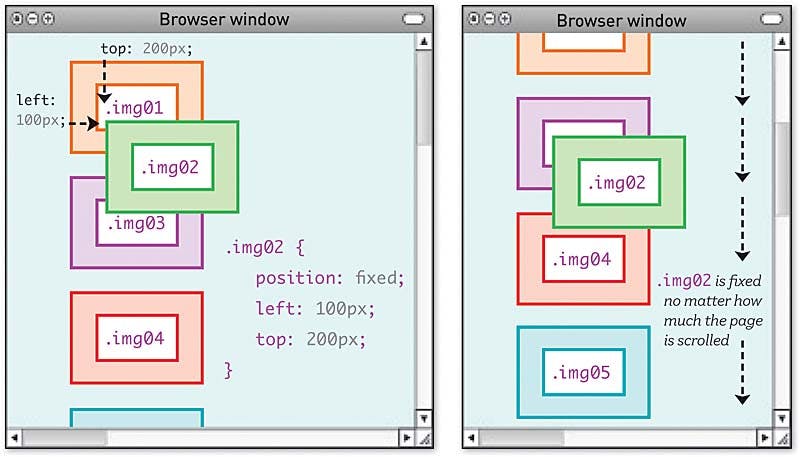
3.CSS Fixed Position Property
An element with
position: fixed;is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled. The top, right, bottom, and left properties are used to position the element.A fixed element does not leave a gap in the page where it would normally have been located.
The Image shows the Fixed CSS Positioning property.
EXAMPLE:
-
In this example, the CSS
fixedproperty of the position has been used.After applying CSS fixed property, the element can not move after the page scroll.
- The Image shows the Fixed CSS Positioning property
4.CSS Absolute Position Property
Absolute positioning is used to position an element relative to the first parent element that has a position other than static. If no such element is found, the containing block is HTML.
With absolute positioning, you can place an element anywhere on a page.
Absolute positioned elements are removed from the normal flow and can overlap elements.
It behaves based on the parent's position.
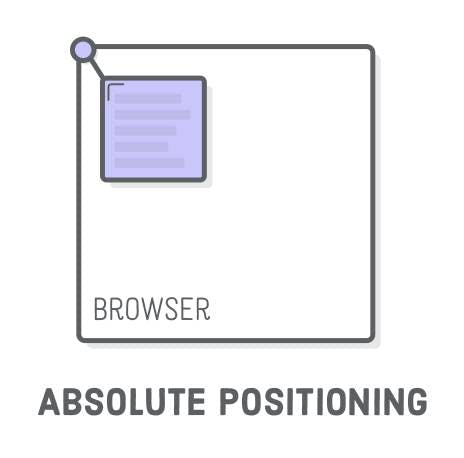
The Image shows the Absolute CSS Positioning property.
Example:
-
In this example, the CSS
absoluteproperty of the position has been used.After applying CSS
absoluteproperty, the element is positioned relative to its nearest positioned element.
5.CSS Stickey Position Property
An element with
position: sticky;is positioned based on the user's scroll position.A sticky element toggles between
relativeandfixed, depending on the scroll position. It is positioned relative until a given offset position is met in the viewport - then it "sticks" in place (like position: fixed).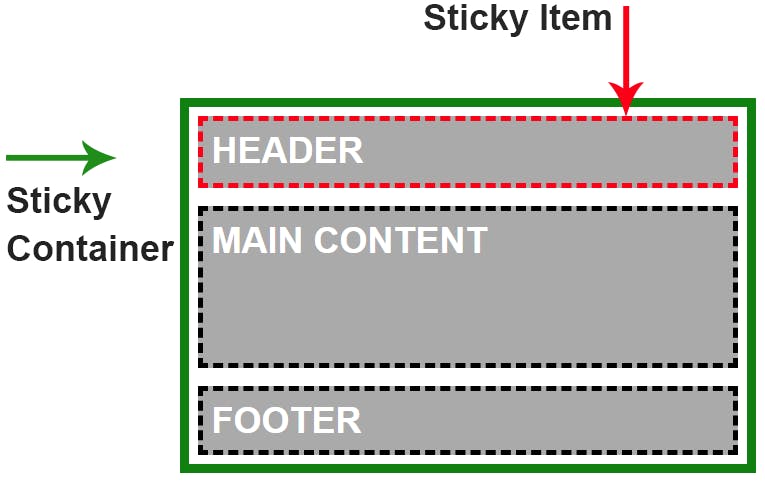
EXAMPLE:
-
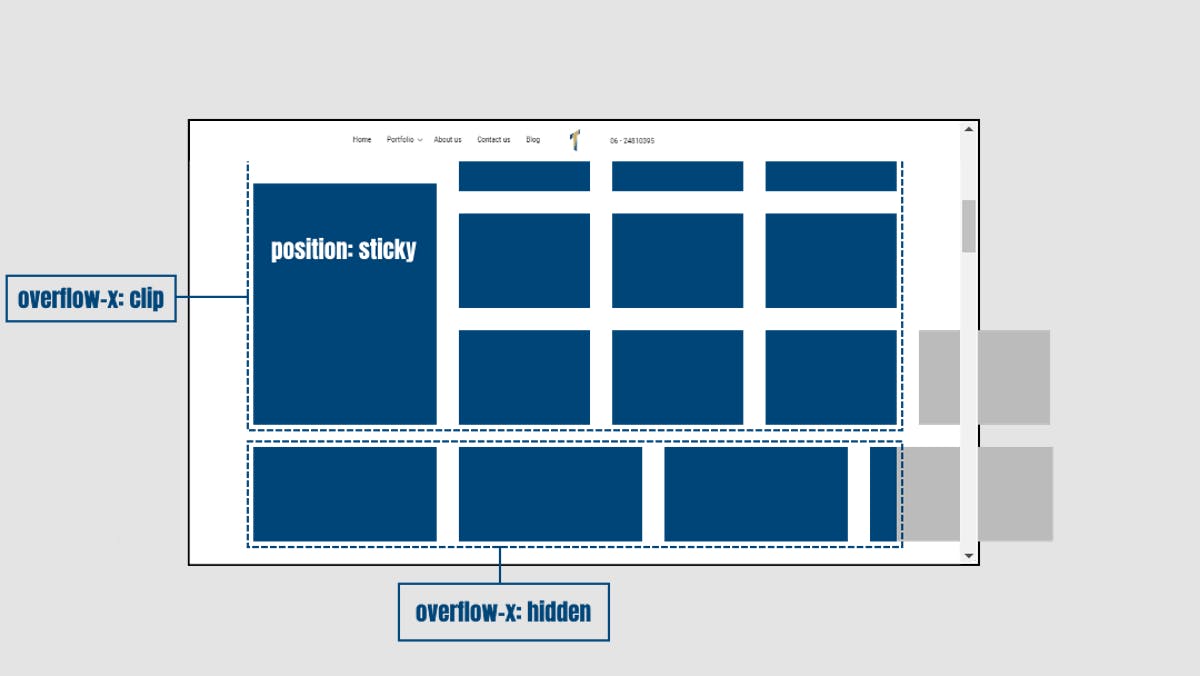
The Image shows the Sticky CSS Positioning property

The Image shows the full review of the CSS Positioning properties